Demonstrative Video
Need for a Diode - Initial Thoughts
Charger Circuit Operation
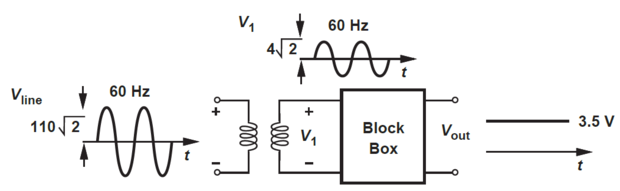
\(\xrightarrow[\text{110 V}]{\text{ac voltage}}\) \(\xrightarrow[\text{4 V}]{\text{Transformer}}\) \(\xrightarrow[\text{3.5 V}]{\text{dc voltage using LPF}}\)
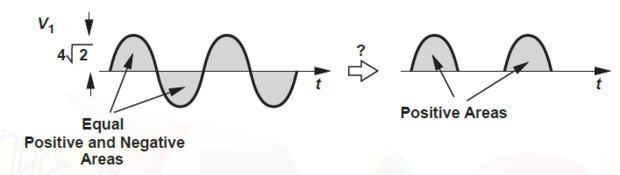
Output of TF using black box exhibits a zero dc content as -ve and +ve half cycles enclose equal areas, leading to a zero average
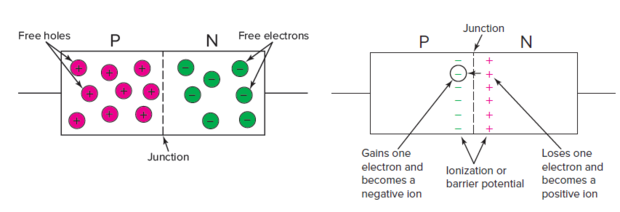
DIODE - Basic Ideas
Resistor \(\rightarrow\) linear device \(\rightarrow\) current Vs voltage is a straight line.
Diode \(\rightarrow\) nonlinear device \(\rightarrow\) \(I\) Vs \(V\) is not a straight line.
- The reason is the barrier potential.
 \[\boxed{V_d < V_b \rightarrow I_d \downarrow} \qquad \boxed{V_d > V_b \rightarrow I_d \uparrow}\]
\[\boxed{V_d < V_b \rightarrow I_d \downarrow} \qquad \boxed{V_d > V_b \rightarrow I_d \uparrow}\]
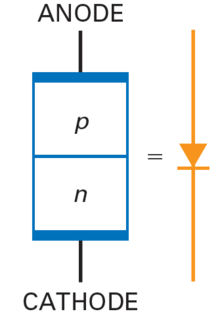
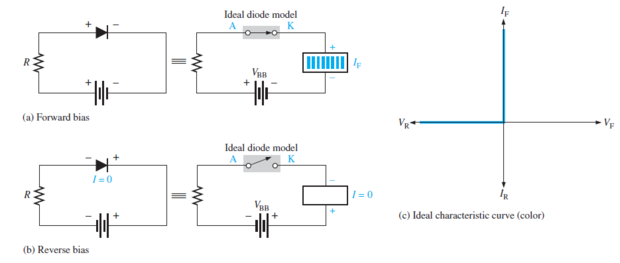
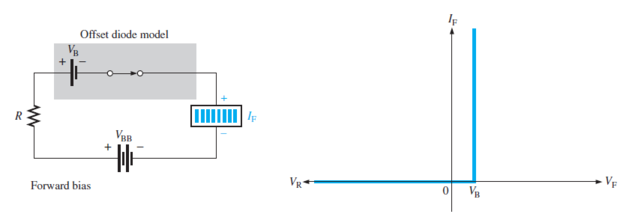
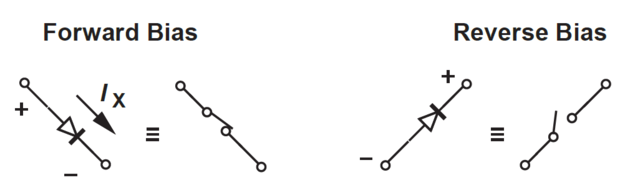
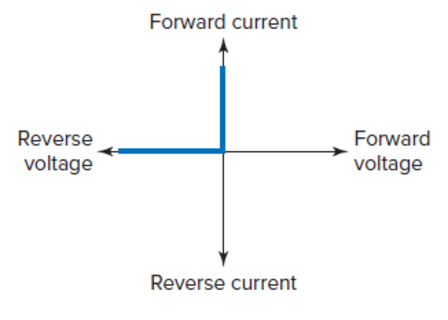
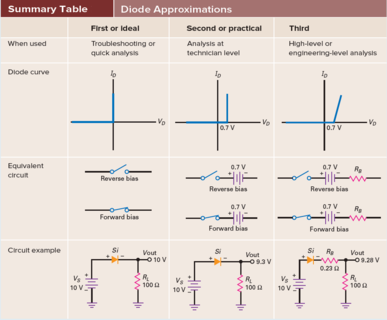
Ideal Diode: acts like a perfect conductor (zero resistance) when forward biased and like a perfect insulator (\(\infty\) resistance) when reverse biased.
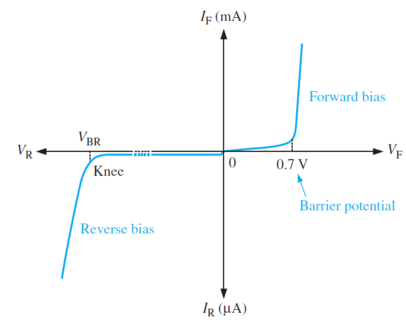
Diode Characteristic Curve
Real
diode
Ideal
diode
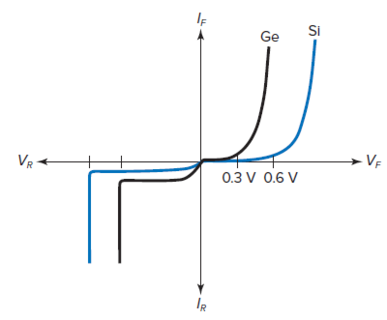
Si Vs
Ge
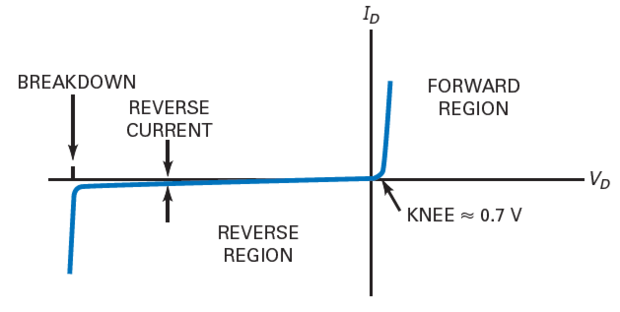
Above the knee voltage, the diode current increases rapidly.
Small increase in the diode voltage cause large increases in diode current.
- \[\text{Bulk resistance}~R_B = R_p + R_n\]. is less than 1 depends on the size of the p and n regions and how heavily doped they are. Often, Bulk Resistance :
Maximum DC Forward Current : If the current in a diode is too large, the excessive heat can destroy the diode. The \(I_{F(max)}\) is one of the maximum ratings given on a data sheet.
- \[\begin{aligned} P_D & = V_D \cdot I_D \\ P_{max} & = V_{max} \cdot I_{max} \end{aligned}\]The power rating is the maximum power the diode can safely dissipate without shortening its life or degrading its propertiesPower Dissipation :
Diode Current Equation
When the diode is reverse biased, its current equation may be obtained by changing the sign of the applied voltage \(V\).
- \[I=I_o\left[\mathrm{e}^{\left(-V / \eta V_T\right)}-1\right]\]Thus, the diode current with reverse bias is
If \(V \gg V_T\), then the term \(\mathrm{e}^{\left(-V / \eta v_T\right)} \ll 1\), therefore \(I \approx-I_o\), termed as reverse saturation current, which is valid as long as the external voltage is below the breakdown value.
Effect of temperature:
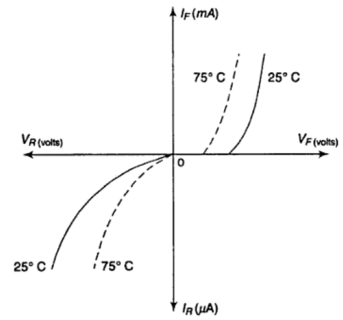
T \(\uparrow~\Rightarrow\) generation of e-p pairs increases, which increase the conductivities
If T \(\uparrow\) at fixed V \(\Rightarrow\) I increases
To bring I to normal \(\Rightarrow\) V \(\downarrow\)
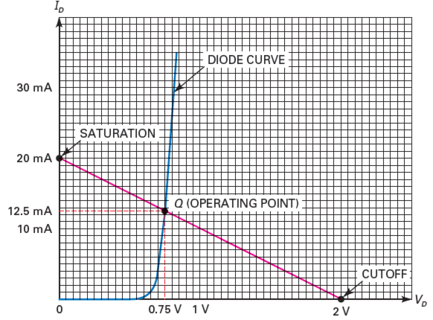
Load Lines
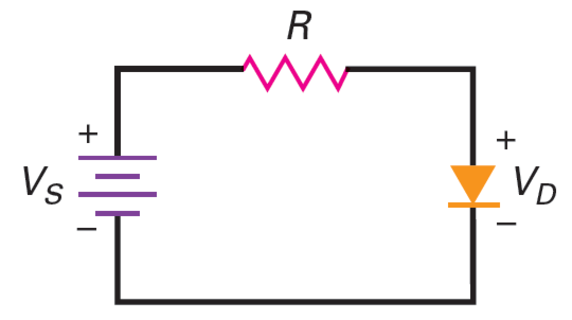
- \[I_D=\frac{V_S-V_D}{R_s}\]Load line
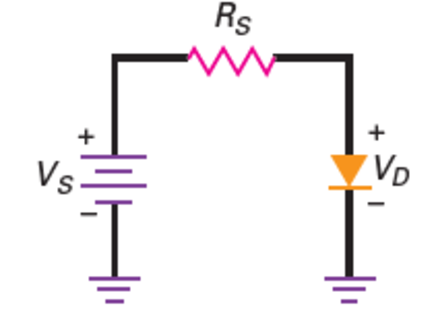
If \(V_s = 2~\mathrm{V}\), \(R = 100~\Omega\)
\(V_D = 0 \Rightarrow I_D = 20~\mathrm{mA}\)
\(I_D = 0 \Rightarrow V_D = V_s = 2~\mathrm{V}\)
The straight line is called the load line
\(Q\) is an abbreviation for quiescent, which means “at rest.”