Demonstrative Video
The Atom
Matter \(\Rightarrow\) Atoms \(\Rightarrow\) electrons, protons, and neutrons (except normal hydrogen does not have a neutron )
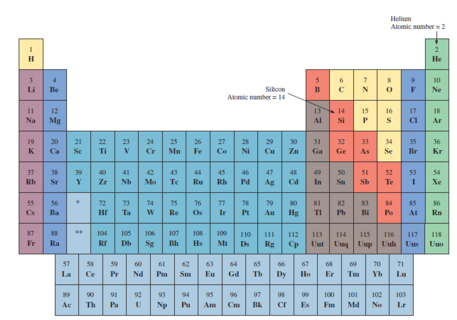
Periodic table \(\Rightarrow\) Elements \(\Rightarrow\) unique atomic structure
All atoms within a given element have the same number of protons.
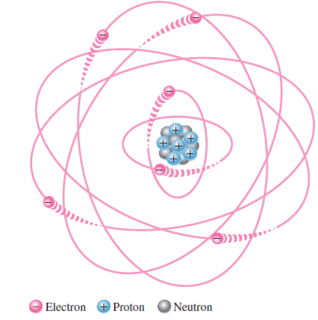
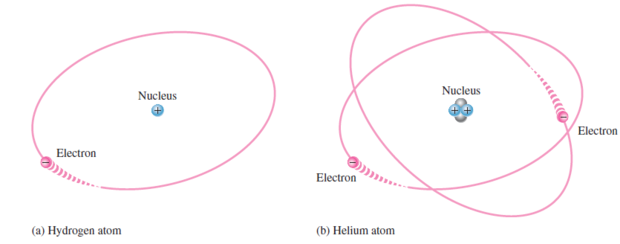
Atom is not a single particle but made up of small dense nucleus around which electrons orbit at a greater distance
Niels Bohr model \(\Rightarrow\) Planetary model \(\Rightarrow\) electrons in an atom circle the nucleus in different orbits similar to solar system
Quantum model is a more accurate representation, but difficult to visualize
For most practical purposes in electronics, the Bohr model suffices and is commonly used because it is easy to visualize.
The Bohr Model
Each of the known 118 elements has unique atomic structure
Protons : positively charged
Neutrons : uncharged particles
Electrons : negatively charged
Atomic Number
Elements arranged in periodic table according to atomic number
Atomic number = number of protons in the nucleus = number of electrons (electrically balanced or neutral atom)
Electrons shells
Electrons near the nucleus have less energy than those in more distant orbits
Separate and distinct energy values exists for electrons
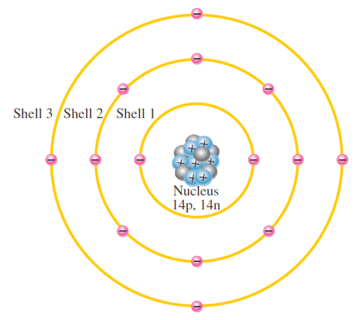
Each discrete distance (orbit) correspond to certain energy level
Orbits are grouped into energy levels known as shells
A given atom has fixed number of shells and each shell has fixed number of electrons
Shell or energy levels are designated as 1, 2, 3...with 1 closest to the nucleus
Valence electrons
Electrons in farther orbit from nucleus have higher energy and less tightly bound to nucleus than the closer orbit electrons
Force of attraction between positively charged nucleus and negatively charged electrons decreases with increasing distance from the nucleus
Outermost shell (valence shell) and electrons present in it (valence electrons)
Valence electrons have highest energy and loosely bound to the atom
Contribute to chemical reaction and bonding within material structure and determine electrical properties
Valence electrons gain sufficient energy from external source and beaks free from atom which is the basis for conduction in materials
Ionization
Atom absorb energy from heat source or light \(\Rightarrow\) electron energy raised \(\Rightarrow\) loosely bound valence electrons jump higher energy shells \(\Rightarrow\) escape the atom’s influence
The process of losing a valence electron is known as Ionization and the associated required energy Ionization energy
Neutral atom becomes positively charged (more protons than electrons) atom known as positive ion and the escaped valence electron is called free electron
Reverse process when free electron collide atom releasing energy forming negative ion
The Quantum Model
Quantum model (recent model) more accurate is a statistical model but difficult to visualize or understand
Comparison to Bohr model
Similarity : nucleus of protons and neutrons surrounded by electrons.
Dis-similarity : electrons do not exist in precise circular orbits as particles
Two important theories:
Wave-particle duality :
Dual characteristics of electron similar to light i.e wave and particle (photon).
The orbiting electron velocity considered to be the wavelength which interfere with the neighbouring electron waves by amplifying or cancelling it
Uncertainly principle :
Electron waves will have peaks and valleys and hence cannot determine its position.
Heisenberg states that simultaneous determination of position and velocity of an electron with certainty is impossible.
Principle result in concept of probability clouds, which are mathematical description of where electrons are located in an atom
In quantum model, each shell or energy level consists of four-subshells called orbitals (\(s,~p,~d,~f\))
- \[\begin{aligned} s & \rightarrow~2~\text{electrons} \\ p & \rightarrow~6~\text{electrons} \\ d & \rightarrow~10~\text{electrons} \\ f & \rightarrow~14~\text{electrons} \\ \end{aligned}\]Maximum electrons that can present in orbitals:

Each shell in the Bohr model is a 3D space surrounding the atom that represents the mean energy of the electron cloud.
Electron cloud (probability cloud) is the area around an atom’s nucleus where an electron will probably be found
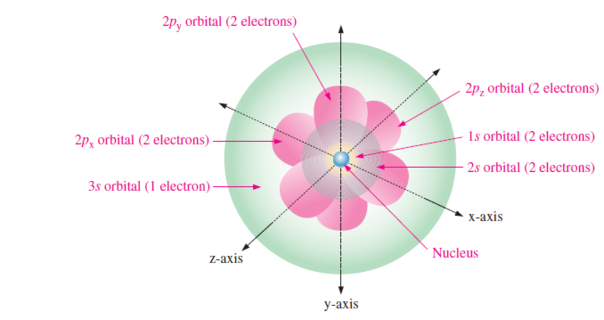
Quantum model of Sodium atom
s-orbitals are shaped like spheres with the nucleus in the center.
Energy level 1, the sphere is “solid”
Energy levels 2 or more, each single s-orbital is composed of spherical surfaces that are nested shells.
A p-orbital for shell 2 has the form of two ellipsoidal lobes with a point of tangency at the nucleus (referred dumbbell shape)
The three p-orbitals in each energy level are oriented at right angles (x-y-z axis) to each other.