Demonstrative Video
Problem-1
A common base pnp transistor amplifier has an input resistance of \(20~\Omega\) and output resistance of \(100~\mathrm{k} \Omega\). The collector load is \(1~\mathrm{k} \Omega\). If a signal of 500 mV is applied between emitter and base, find the voltage amplification. Assume \(\alpha\) to be nearly one.
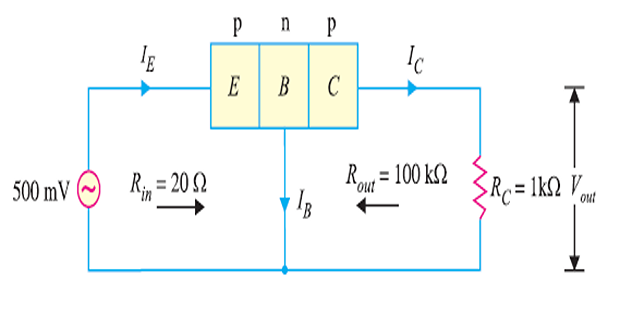
\[\begin{aligned} I_E & = \dfrac{V_s}{R_{in}} = \dfrac{500~\mathrm{mV}}{20~\Omega} = 25~\mathrm{mA}\\ \alpha & = 1~\Rightarrow ~I_C = I_E = 25~\mathrm{mA}\\ \Rightarrow~A_v & = \dfrac{V_{out}}{V_s} = \dfrac{25~\mathrm{V}}{500~\mathrm{mV}} = 50 \end{aligned}\]
Problem-2
In a common base connection, current amplification factor is 0.9. If the emitter current is 1mA, determine the value of base current.
\[\begin{aligned} \alpha & = 0.9 \qquad I_E = 1~\mathrm{mA} \\ \alpha & = \dfrac{I_C}{I_E}\\ \Rightarrow~I_C & = \alpha \cdot I_E = 0.9 \times 1 = 0.9~\mathrm{mA} \\ I_B & = I_E - I_C = 1-0.9 = 0.1~\mathrm{mA} \end{aligned}\]
Problem-3
In a common base connection, \(\alpha = 0.95\). The voltage drop across \(2~ \mathrm{k}\Omega\) resistance which is connected in the collector is 2 V. Find the base current.
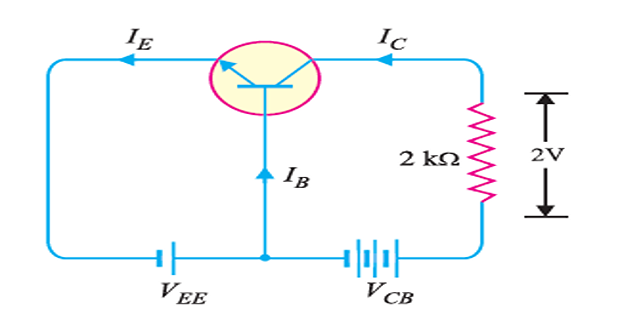
\[\begin{aligned} I_C & = \dfrac{2~V}{2~\mathrm{k}\Omega} = 1~\mathrm{mA} \\ I_E & = \dfrac{I_C}{\alpha} = \dfrac{1}{0.95} = 1.05~\mathrm{mA} \\ I_B & = I_E - I_C = 1.05-1 = 0.05~\mathrm{mA} \end{aligned}\]
Problem-4
Determine \(I_C\) and \(V_{CB}\) assuming silicon transistor.

\[\begin{aligned} V_{BE} & = 0.7~\mathrm{V}~\Leftarrow~\text{Silicon transistor}\\ V_{EE} & = I_E \cdot R_E + V_{BE}~\Leftarrow~\text{KVL} \\ \Rightarrow~I_E & = \dfrac{V_{EE}-V_{BE}}{R_E} = \dfrac{8V-0.7V}{1.5~\mathrm{k}\Omega} = 4.87~\mathrm{mA}\\ \Rightarrow~I_C & \approx I_E = 4.87~\mathrm{mA}\\ V_{CC} & = I_C \cdot R_C + V_{CB}~\Leftarrow~\text{KVL} \\ \Rightarrow~V_{CB} & = V_{CC}-I_C \cdot R_C\\ & = 18V-4.87~\mathrm{mA} \times 1.2~\mathrm{k}\Omega = 12.16~\mathrm{V} \end{aligned}\]
Problem-5
Calculate \(I_E\) of a transistor if \(\beta = 50\) and \(I_B = 20~\mu A\). \[\begin{aligned} \beta & = 50 \qquad I_B = 20~\mu A = 0.02~\mathrm{mA}\\ I_C & = \beta \cdot I_B = 50 \times 0.02 = 1~\mathrm{mA}\\ I_E & = I_B +I_C = 0.02+1 = 1.02~mA \end{aligned}\]
Problem-6
A transistor is connected in common emitter (CE) configuration in which collector supply is 8 V and the voltage drop across resistance \(R_C\) connected in the collector circuit is 0.5 V. The value of \(R_C = 800 ~\Omega\). If \(\alpha = 0.96\), determine : (i) \(V_{CE}\) (ii) \(I_B\)
 \[\begin{aligned}
V_{CE} & = V_{CC}-0.5 \\
&= 8-0.5 = 7.5~\mathrm{V}\\
I_C & = \dfrac{0.5~V}{800~\Omega} = 0.625~\mathrm{mA}\\
\beta & = \dfrac{\alpha}{1-\alpha}=\dfrac{0.96}{1-0.96}=24\\
I_B & = \dfrac{I_C}{\beta}=\dfrac{0.625}{24}=0.026~\mathrm{mA}
\end{aligned}\]
\[\begin{aligned}
V_{CE} & = V_{CC}-0.5 \\
&= 8-0.5 = 7.5~\mathrm{V}\\
I_C & = \dfrac{0.5~V}{800~\Omega} = 0.625~\mathrm{mA}\\
\beta & = \dfrac{\alpha}{1-\alpha}=\dfrac{0.96}{1-0.96}=24\\
I_B & = \dfrac{I_C}{\beta}=\dfrac{0.625}{24}=0.026~\mathrm{mA}
\end{aligned}\]
Problem-7
Determine \(V_{CB}\) if the transistor is of silicon and has \(\beta = 150\).
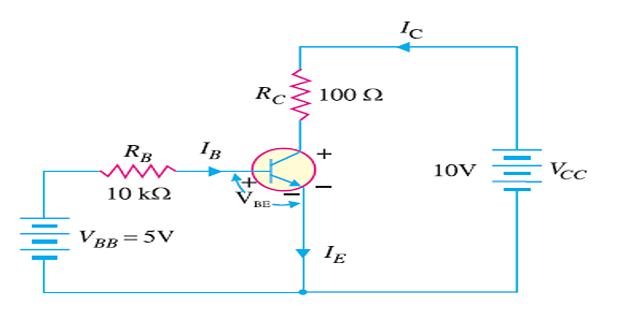
\[\begin{aligned} &V_{BB}-I_B \cdot R_B - V_{BE} =0 ~\Leftarrow~\text{KVL} \\ \Rightarrow~I_B & = \dfrac{V_{BB}-V_{BE}}{R_B} = \dfrac{5V-0.7V}{10~k\Omega} = 430~\mu A \\ I_C & = \beta \cdot I_B = 150\times 430~\mu A = 64.5~\mathrm{mA} \\ V_{CE} & = V_{CC}-I_C\cdot R_C \\ & = 10V-64.5~\mathrm{mA} \times 100~\Omega = 3.55~\mathrm{V}\\ V_{CB} & = V_{CE}-V_{BE} = 3.55-0.7=2.85~\mathrm{V} \end{aligned}\]
Problem-8
If \(V_{CC}=12~\mathrm{V}\) and \(R_C = 6~k\Omega\), then determine the Q-point if zero signal \(I_B = 20~\mu A\) and \(\beta = 50\).
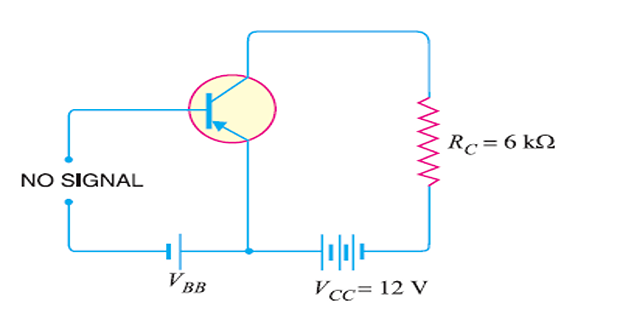
\[\begin{aligned} V_{CE}&=V_{CC}-I_C \cdot R_C\\ \Rightarrow~I_C & = 0 \rightarrow V_{CE}=V_{CC} = 12~V \\ \Rightarrow~V_{CE}&=0~\rightarrow~I_C = \dfrac{V_{CC}}{R_C} = \dfrac{12~\mathrm{V}}{6~k\Omega} = 2~\mathrm{mA}\\ I_B & = 20~\mu A = 0.02~\mathrm{mA} \\ I_C & = \beta \cdot I_B = 50\times 0.02 = 1~\mathrm{mA} \\ V_{CE} & = V_{CC}-I_{C}\cdot R_C \\ &= 12-1~\mathrm{mA} \times 6~k\Omega = 6~\mathrm{V} \end{aligned}\]
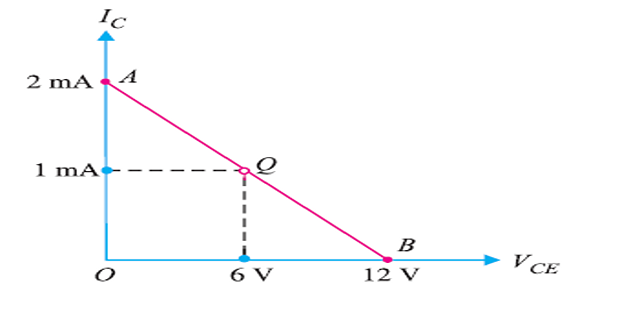 \[\begin{aligned}
Q & = (6~\mathrm{V},~1~\mathrm{mA})
\end{aligned}\]
\[\begin{aligned}
Q & = (6~\mathrm{V},~1~\mathrm{mA})
\end{aligned}\]
Problem-9
Determine \(I_B~I_C,~I_E\) and \(V_{CE},~V_{CB},~V_{BE}\)
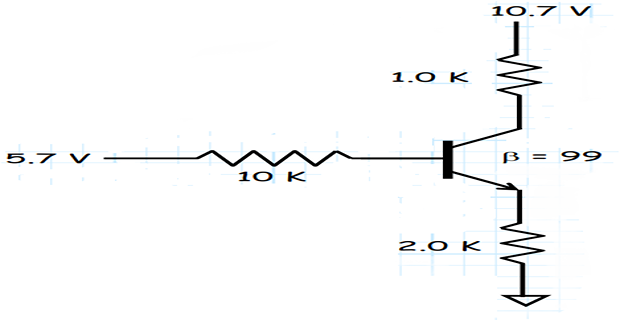
\[\begin{aligned} V_{BE} & = 0.7~\mathrm{V} \\ I_C &= \beta \cdot I_B = 99I_B\\ I_E & = (\beta+1)\cdot I_B = 100\cdot I_B\\ & 5.7-10I_B-V_{BE}-2I_E = 0 ~\Leftarrow~\text{KVL} \\ \Rightarrow~I_B & = \dfrac{5}{210} = 23.8~\mathrm{mA}~\Leftarrow~\text{On Substitution} \\ I_C & = \beta \cdot I_B = 2.356 ~\mathrm{mA}\\ I_E & = 100 \cdot I_B = 2.380~\mathrm{mA}\\ V_C & = 10.7-I_C \times 1=8.34~\mathrm{V}\\ V_E & = 0+I_E \times 2 = 4.76~V\\V_{CE}& = V_C-V_E = 3.58~\mathrm{V}\\ V_{CB}& = V_{CE} – V_{BE} = 2.88~\mathrm{V} \end{aligned}\]