Solved Problems on Source Transformation
Demonstrative Video
Problem-1
Find \(i_a\) by simplifying the circuit using Source Transformation ?
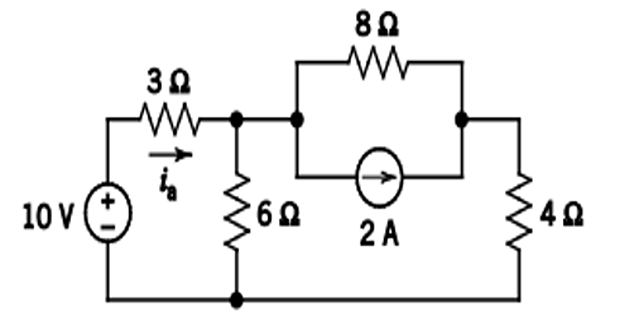
Solution-1
Step-1:
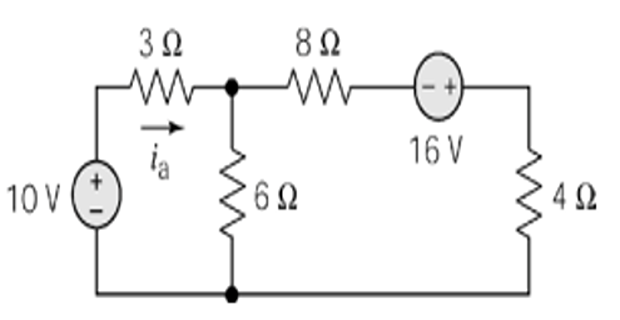
Step-2:
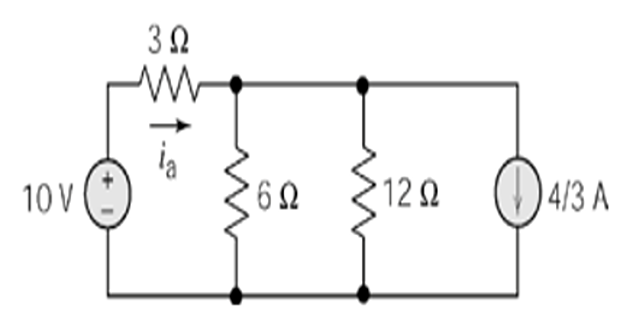
Step-3:
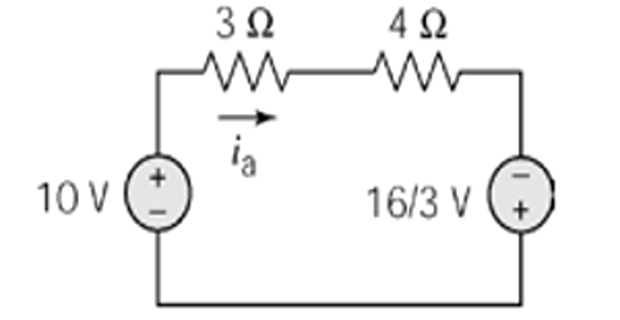
\[\begin{aligned} \text{KVL} & \Rightarrow -10+3i_a+4i_a-16/3 = 0 \\ i_a & = 2.19~\mathrm{A} \end{aligned}\]
Problem-2
Find \(i_{R2}\) by simplifying the circuit using Source Transformation ?
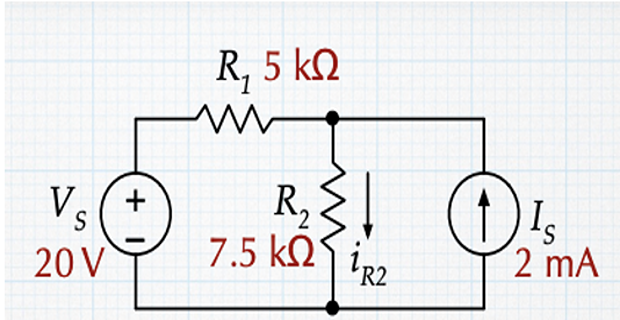
Solution-2
Step-1
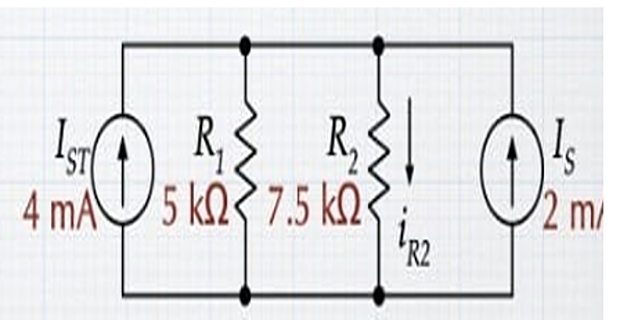 \[\begin{aligned}
I_{ST} & = V_s/R_1
=20/5 = 4~\mathrm{mA}
\end{aligned}\]
\[\begin{aligned}
I_{ST} & = V_s/R_1
=20/5 = 4~\mathrm{mA}
\end{aligned}\]
Step-2
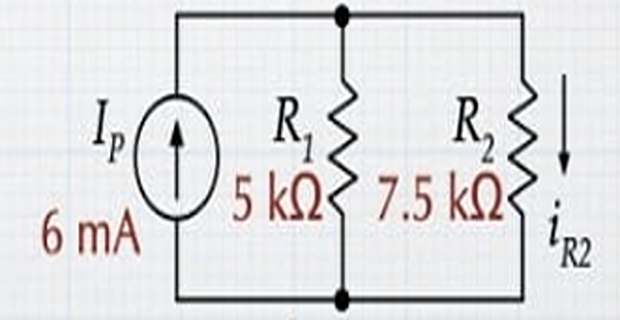 \[\begin{aligned}
I_P & = I_{ST}+I_S
= 6~\mathrm{mA}
\end{aligned}\]
\[\begin{aligned}
I_P & = I_{ST}+I_S
= 6~\mathrm{mA}
\end{aligned}\]
\[\begin{aligned} \text{Current division}~i_{R2} & = \dfrac{R_1}{R_1+R_2} \times I_P = 2.4~\mathrm{mA} \end{aligned}\]
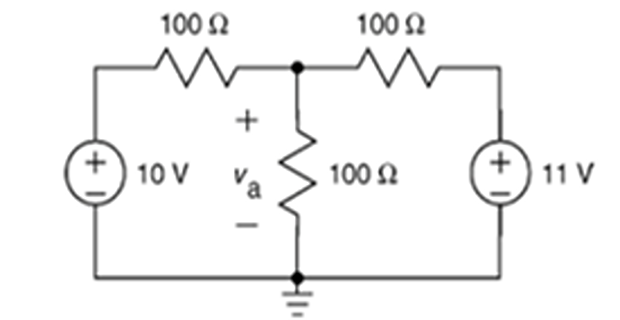
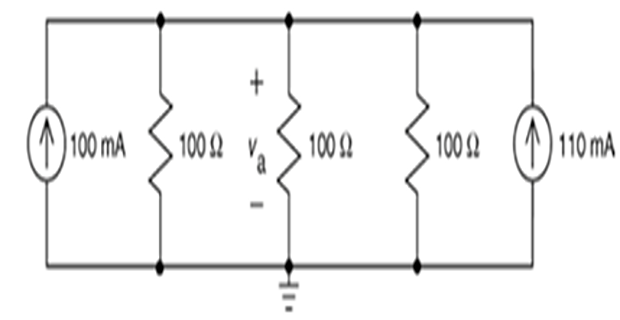
Problem-3
Find \(v_a\) using Source Transformation ?
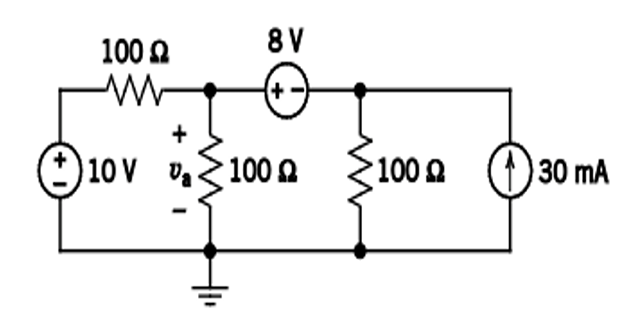
Solution-3
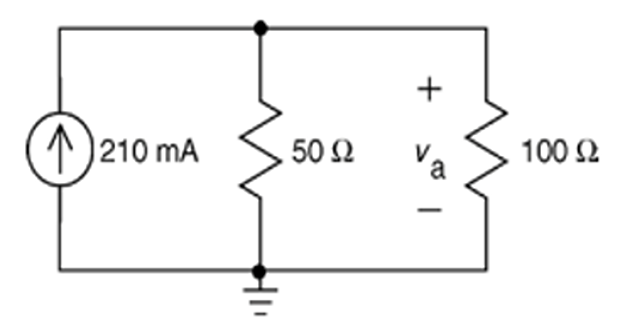 \[\begin{aligned}
v_a & = \dfrac{50\times 100}{50+100}\times 0.21
= 7~\mathrm{V}
\end{aligned}\]
\[\begin{aligned}
v_a & = \dfrac{50\times 100}{50+100}\times 0.21
= 7~\mathrm{V}
\end{aligned}\]
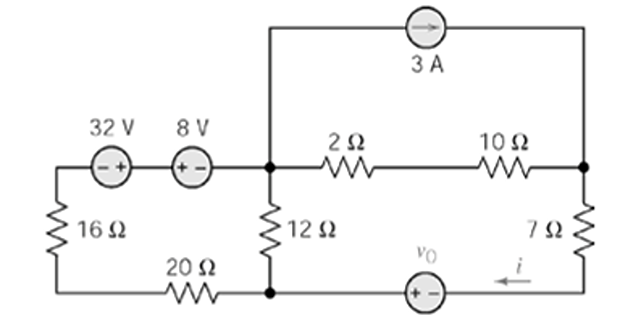
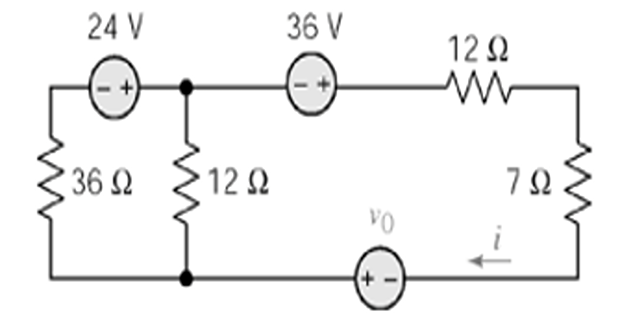
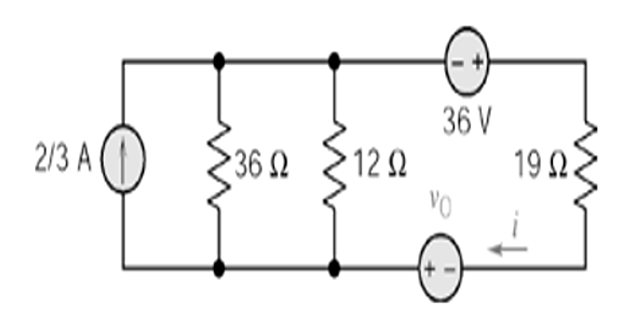
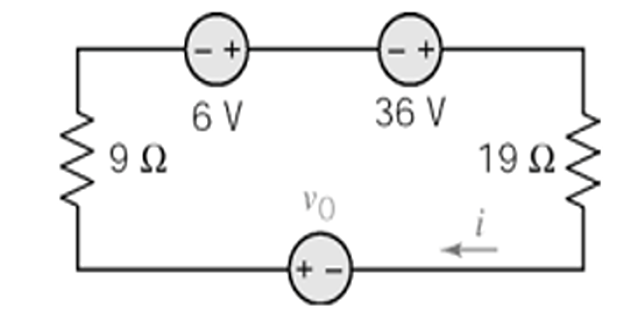
Problem-4
Find \(v_0\) if \(i=5/2\) A, using Source Transformation ?
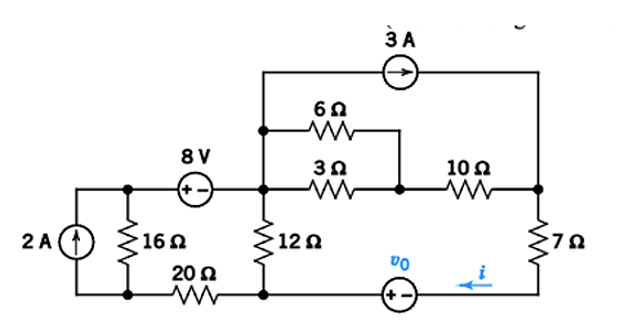
Solution-4
 \[\begin{aligned}
\text{KVL}~&-6+i(9+19)-36-v_0=0\\
i&=5/2~(\text{Given})\\
v_0&=-42+28(5/2) = 28~\mathrm{V}
\end{aligned}\]
\[\begin{aligned}
\text{KVL}~&-6+i(9+19)-36-v_0=0\\
i&=5/2~(\text{Given})\\
v_0&=-42+28(5/2) = 28~\mathrm{V}
\end{aligned}\]
Problem-5
Obtain a single current source for the network shown below and get the magnitude of current source and the resistor of the circuit.
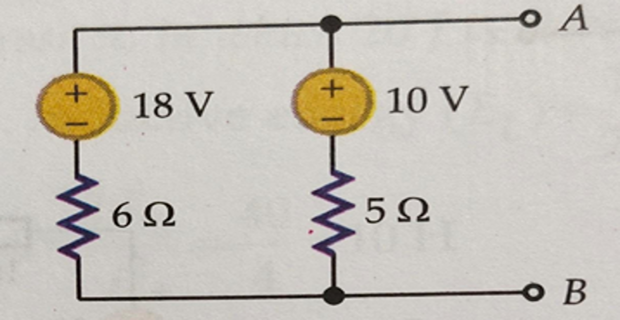
Solution-5
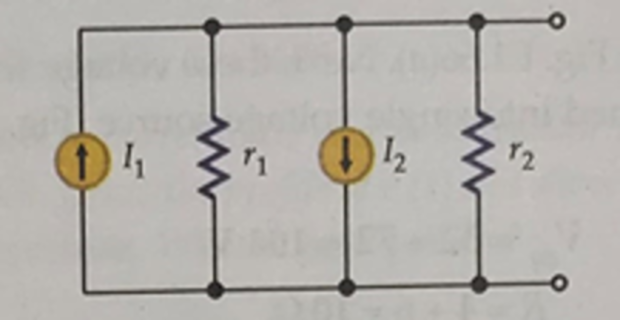
\[\begin{aligned} I_1 & = \dfrac{18}{6} = 3~\mathrm{A} \\ I_2 & = \dfrac{10}{5} = 2~\mathrm{A} \\ r_1 & = 6~\Omega \quad r_2 = 5~\Omega \\ I_{eq} & = I_1 - I_2 = 1~\mathrm{A} \\ R & = \dfrac{r_1 \cdot r_2}{r_1 + r_2} = 2.73~\Omega \end{aligned}\]