Demonstrative Video
Concept of Electric Potential
Finding Electric Potential From Electric Field
Voltage
To move the electron in a conductor in a particular direction requires some work or energy transfer.
This work is performed by an external electromotive force (emf), also known as voltage or potential difference.
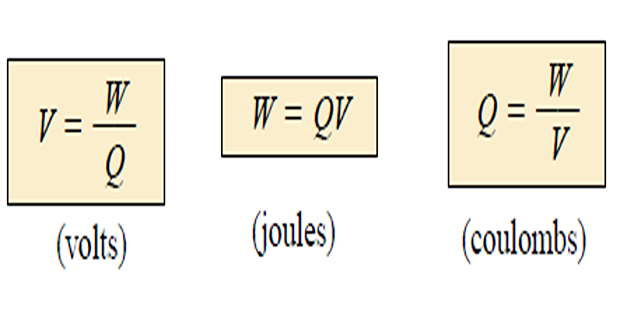
- \[v_{a b} \triangleq \frac{d w}{d q}\]\(q\)\(w\)The voltage between two points a and b in an electric circuit is the energy (or work) needed to move a unit charge from a to b;
- \[1 \text { volt }=1 \text { joule/coulomb }=1 \text { newton-meter/coulomb }\]It is evident
Voltage (or potential difference) is the energy required to move a unit charge through an element, measured in volts (V).
PD of 1 volt (V) exists between two points if 1 joule (J) of energy is exchanged in moving 1 coulomb (C) of charge between the two points.
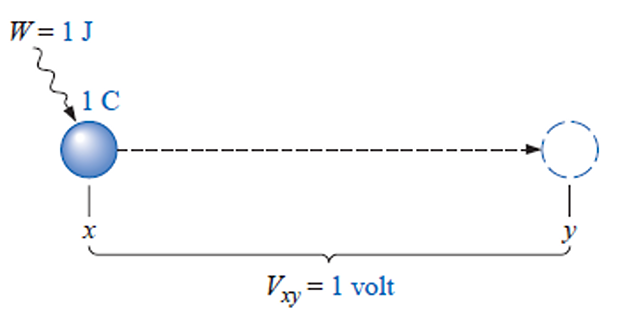
- Mathematically,
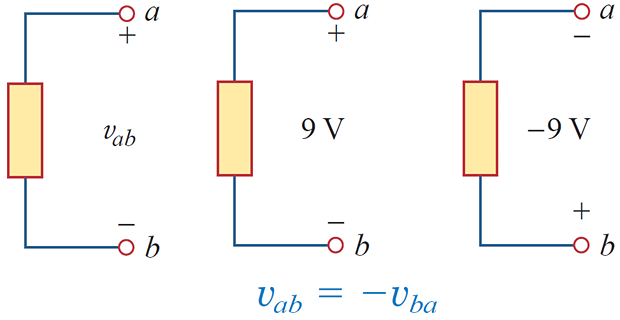
Potential difference or voltage is always measured between two points in the system.
Changing either point may change the potential difference between the two points under investigation.
Like electric current, a constant voltage is called a dc voltage whereas a sinusoidally time-varying voltage is called an ac voltage.
A dc voltage is commonly produced by a battery; ac voltage is produced by an electric generator.
Power and Energy
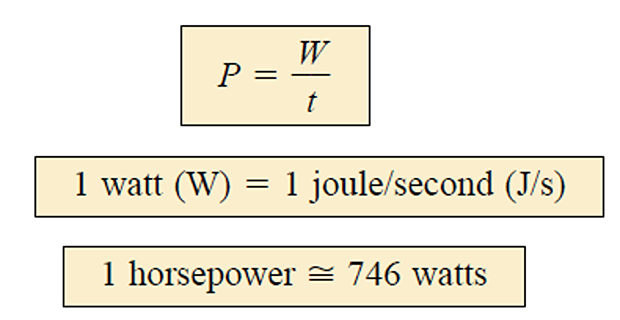
Power is an indication of how much work (the conversion of energy from one form to another) can be done in a specified amount of time, that is, a rate of doing work.
Power is the time rate of expending or absorbing energy, measured in watts (W).
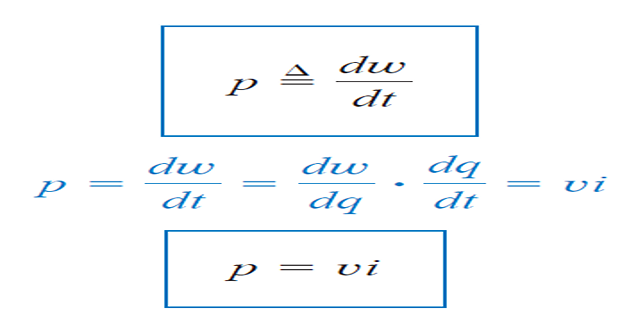
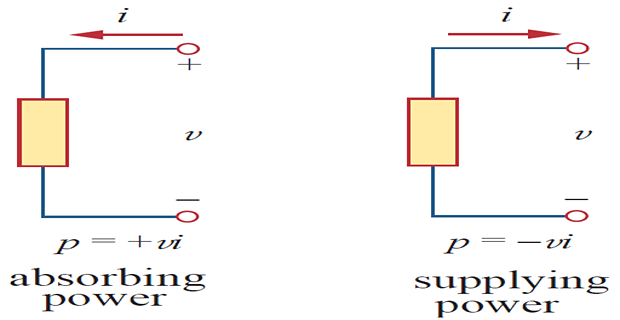
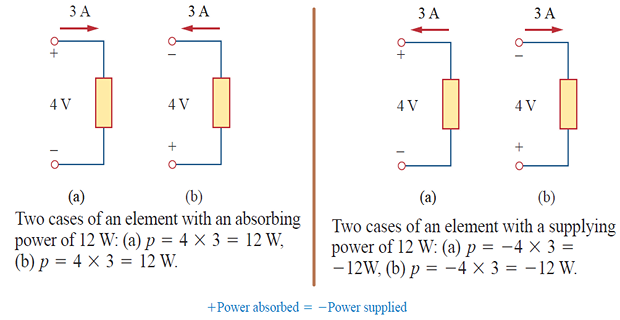
Passive sign convention is satisfied when the current enters through the positive terminal of an element and \(p=+v i\). If the current enters through the negative terminal, \(p=-v i\).
Law of conservation of energy must be obeyed in any electric circuit.
- \[\boxed{\sum P =0}\]For this reason, the algebraic sum of power in a circuit, at any instant of time, must be zero
Thus, the total power supplied to the circuit must balance the total power absorbed.
- \[w=\int_{t_{0}}^{t} p ~d t=\int_{t_{0}}^{t} v i~ d t\]Energy absorbed or supplied by an element
Energy is the capacity to do work, measured in joules (J).
- \[1~ Wh = 3600 ~J\]The electric power utility companies measure energy in watt-hours (Wh)
Resistance
The flow of charge through any material encounters an opposing force similar in many respects to mechanical friction.
This opposition, due to the collisions between electrons and between electrons and other atoms in the material, which converts electrical energy into another form of energy such as heat, is called the resistance of the material.
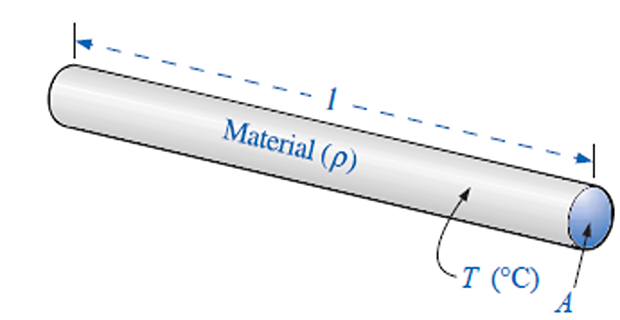
The resistance of any material with a uniform cross-sectional area is determined by the following four factors:
Material
Length
Cross-sectional area
Temperature
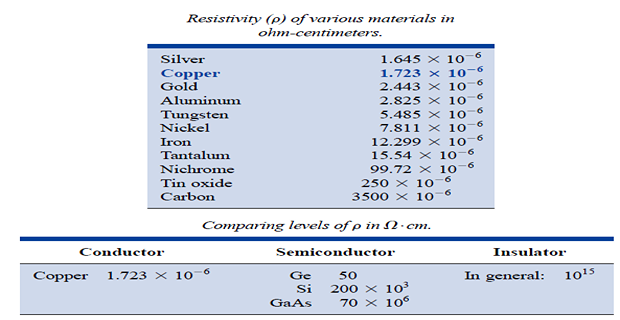
The resistance of a material depends on a property called resistivity, denoted by \(\rho\)

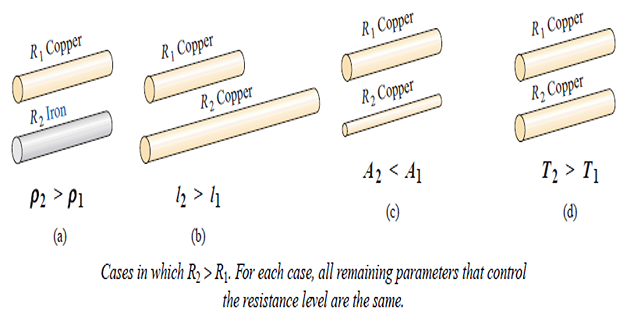
\(\rho \uparrow \Rightarrow R \uparrow\)
\(l \uparrow \Rightarrow R \uparrow\)
\(A \downarrow \Rightarrow R \uparrow\)
\(T \uparrow \Rightarrow R \uparrow\)
Effect of Temperature on Resistance
Conductors:
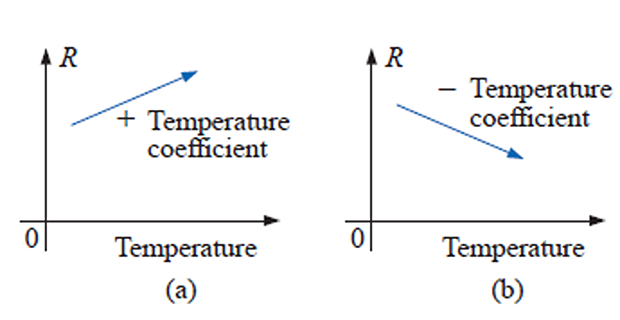
for good conductors, an increase in temperature will result in an increase in the resistance level. Consequently, conductors have a positive temperature coefficient.
Semi-conductors:
for semiconductor materials, an increase in temperature will result in a decrease in the resistance level. Consequently, semiconductors have negative temperature coefficients
Insulators:
As with semiconductors, an increase in temperature will result in a decrease in the resistance of an insulator. The result is a negative temperature coefficient.
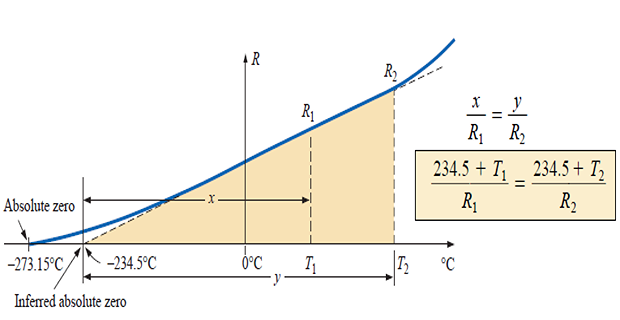
Determining Resistance of a material
\(R\) increases almost linearly with an increase in \(T\)
It is important to determine \(R\) at any \(T\) within operating limits.
Although the actual curve extends to absolute zero (\(-273.15^{\circ}C\), or 0 K), the straight-line approximation is quite accurate for the normal operating temperature range
From similar triangles:
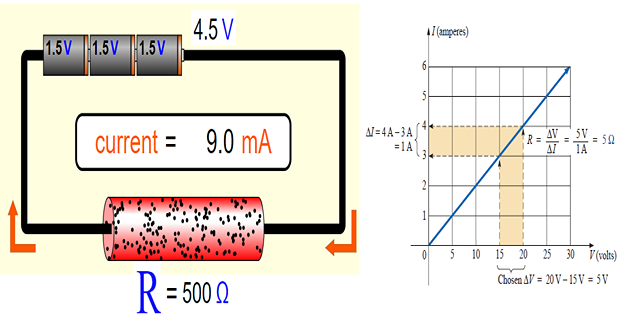
Ohm’s Law:
- \[\boxed{v \propto i}\]flowing through the resistor. across a resistor is directly proportional to the current Ohm’s law states that the voltage
- \[\boxed{v=iR}\]Constant of proportionality for a resistor to be the resistance, R.
Revisiting Power

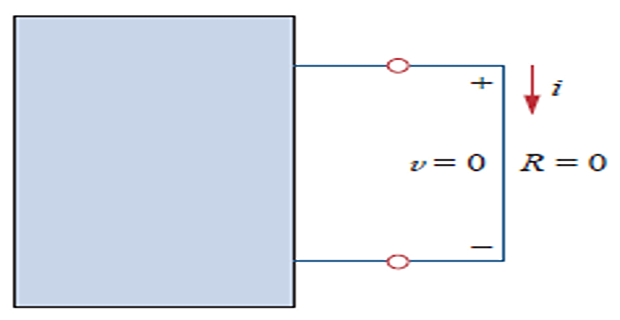
Open Circuit and Short Circuit
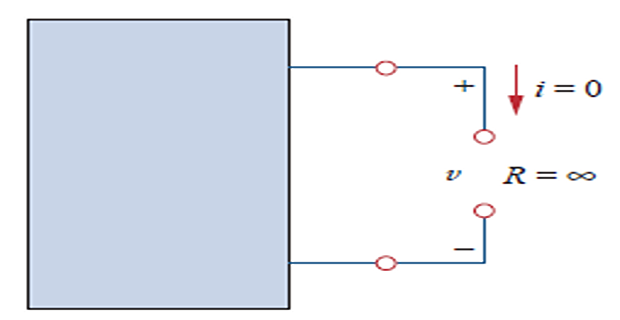
Open-Circuit: circuit element with resistance approaching infinity
Short-Circuit: circuit element with resistance approaching zero