Demonstrative Video
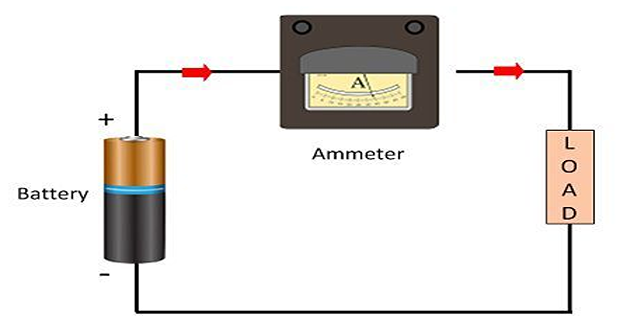
Ammeters

-
The ideal ammeter has zero internal resistance.
-
But practically the ammeter has small internal resistance.
-
The measuring range of the ammeter depends on the value of resistance.
Working Principle & Connection
-
The working principle of an ammeter depends on the current flowing along with its resistance.
-
Very little impedance is used inside the ammeter as it must drop the least amount of voltage attached to it.
-
It is connected to the series of circuits as the current in the series circuit is the same.
Types of Ammeter
-
Depending on their design
-
Permanent moving coil ammeter.
-
Moving iron/coil ammeter.
-
Electro-dynamometer ammeter.
-
Rectifier type ammeter.
-
-
By the type of current flowing
-
DC ammeter
-
AC ammeter
-
-
Permanent moving coil ammeter
-
used only for the measurement of the direct current
-
conductor is placed between the pole of the permanent magnet.
-
When the current flows through the coil, it starts deflecting.
-
The deflection of the coil depends on the magnitude of current flows through it.
-
-
Moving iron/coil ammeter
-
measures both the alternating and direct current
-
coil freely moves between the poles of a permanent magnet. When the current passes through the coil, it starts deflecting at a certain angle. The deflection of the coil is proportional to the current passes through the coil.
-
-
Electro-dynamometer ammeter
-
measurement of both AC and DC
-
The accuracy of the instrument is high as compared to the PMMC and MI instrument.
-
The calibration of the instrument is same both for AC and DC, i.e. if DC calibrates the instrument then without re-calibration, it is used for AC measurement.
-
-
Rectifier type ammeter
-
used for measuring the alternating current.
-
The instruments using the rectifying instrument which converts the direction of current and pass it to the PMMC instrument.
-
Such type of instrument is used for measuring the current in the communication circuit.
-
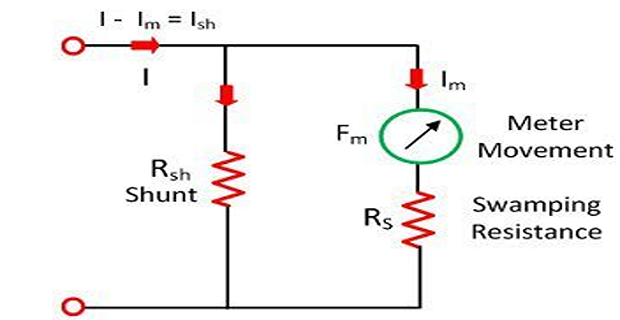
Ammeter Shunt
-
The high current directly passes through the ammeter which damages their internal circuit.
-
This problem can be removed by connecting the shunt resistance in parallel with the ammeter.
-
The major portion of the current passes through the shunt resistance.
-
The shunt resistance will not affect the working of the ammeter, i.e., the movement of the coil remains same.
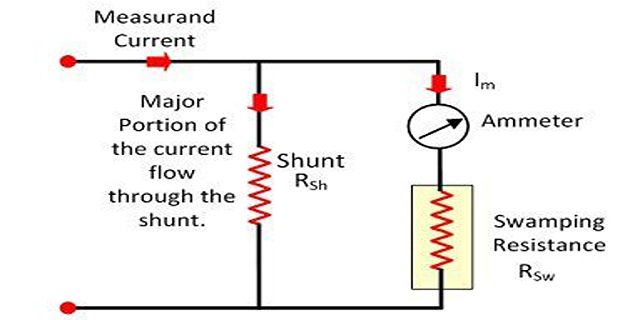
Effect of Temperature in Ammeter
-
Ammeter is sensitive to the surrounding temperature which causes the error in the reading.
-
This can reduce by swamping resistance.
-
The resistance having zero temperature coefficient is known as the swamping resistance.
-
It connects in series with the ammeter.
-
The swamping resistance reduces the effect of temperature on the meter.
-
The ammeter has the inbuilt fuse which protects the ammeter from the heavy current.
-
If substantial current flows through the ammeter, the fuse will break.
-
Ammeter would not measure the current until the fuse is replaced