Phasor Relationships of RLC Elements
Demonstrative Video
Phasor Relationships for Circuit Elements
Resistor :
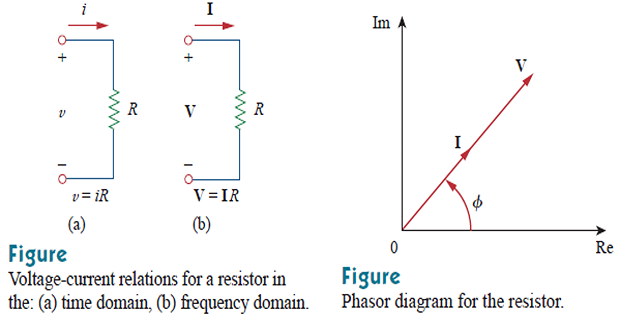
\[\begin{aligned} i &=I_{m} \cos (\omega t+\phi) \quad \Rightarrow \mathbf{I}=I_{m} \angle \phi \\ v &=i R=R I_{m} \cos (\omega t+\phi) \\ \mathbf{V} &=R I_{m} \angle \phi \\ &\boxed{\mathbf{V} =R \mathbf{I}} \end{aligned}\]
Voltage and current are in phase
Inductor :
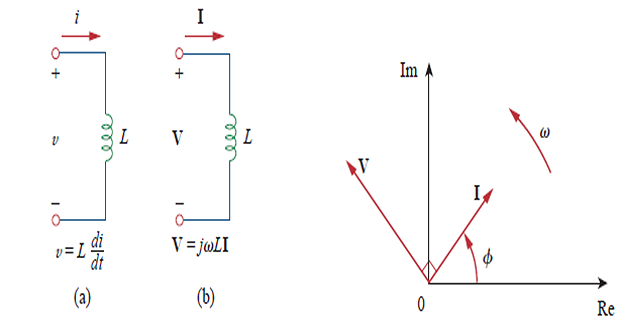
\[\begin{gathered} v=L \frac{d i}{d t}=-\omega L I_{m} \sin (\omega t+\phi) \\ v=\omega L I_{m} \cos \left(\omega t+\phi+90^{\circ}\right) \\ \mathbf{V}=\omega L I_{m} e^{j\left(\phi+90^{\circ}\right)}=\omega L I_{m} e^{j \phi} e^{j 90^{\circ}}=\omega L I_{m} \angle \phi+90^{\circ} \\ \boxed{\mathbf{V}=j \omega L \mathbf{I}} \quad e^{j 90^{\circ}}=j . \end{gathered}\]
Voltage and current are \(90^{\circ}\) out of phase, \(I\) lags \(V\) by \(90^{\circ}\)
Capacitor :
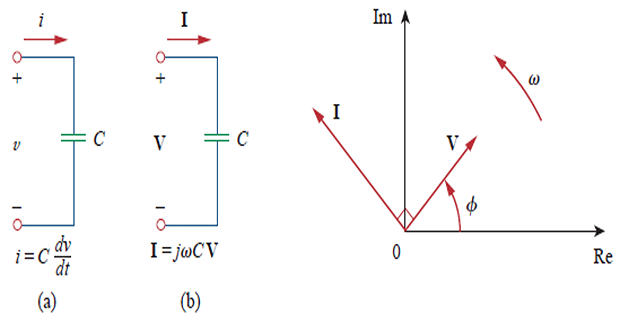 \[\begin{aligned}
i & = C \dfrac{dv}{dt} \\
I & = j\omega C V \Rightarrow \boxed{V =
\dfrac{I}{j\omega C}}
\end{aligned}\]
\[\begin{aligned}
i & = C \dfrac{dv}{dt} \\
I & = j\omega C V \Rightarrow \boxed{V =
\dfrac{I}{j\omega C}}
\end{aligned}\]Voltage and current are \(90^{\circ}\) out of phase, \(I\) leads \(V\) by \(90^{\circ}\)
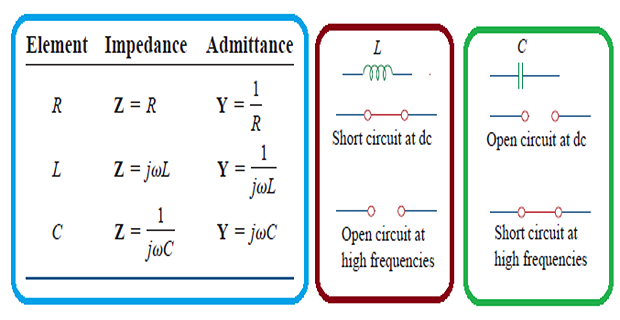
Summary of Relationship
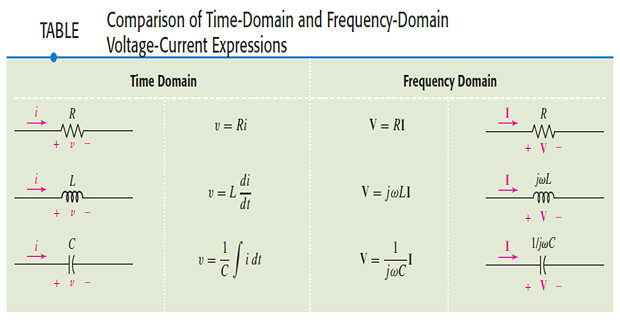
Impedance & Admittance
The ratio of phasor voltage to phasor current \[\frac{\mathbf{V}}{\mathbf{I}}=R, \quad \frac{\mathbf{V}}{\mathbf{I}}=j \omega L, \quad \frac{\mathbf{V}}{\mathbf{I}}=\frac{1}{j \omega C}\]
Ohm’s Law in phasor form for any type of element \[\boxed{\mathbf{Z} = \dfrac{\mathbf{V}}{\mathbf{I}} \Rightarrow \mathbf{V = ZI}}\] where \(\mathbf{Z}~\Rightarrow\) Impedance (in \(\Omega\)) \(\Leftarrow\) frequency-dependent quantity
The impedance \(\mathbf{Z}\) of a circuit is the ratio of the phasor voltage \(\mathbf{V}\) to the phasor current \(\mathbf{I}\), measured in ohms \((\Omega)\).
\(\mathbf{Z}\) : opposition that the circuit exhibits to the flow of sinusoidal current
Although \(\mathbf{Z}\) is the ratio of two phasors, it is not a phasor, because it does not correspond to a sinusoidally varying quantity.
\[\begin{gathered} \boxed{\mathbf{Z}=R+j X=|\mathbf{Z}| \angle \theta } \quad |\mathbf{Z}|=\sqrt{R^{2}+X^{2}}, \quad \theta=\tan ^{-1} \frac{X}{R} \\ \boxed{R=|\mathbf{Z}| \cos \theta} \quad \boxed{X=|\mathbf{Z}| \sin \theta} \\ \boxed{\mathbf{Y}=\frac{1}{\mathbf{Z}}=\frac{\mathbf{I}}{\mathbf{V}} }\\ \mathbf{Y}=G+j B \quad \left(G: \text{Conductance}~B: \text{Susceptance}\right) \\ G+j B=\frac{1}{R+j X} \end{gathered}\] By rationalization, \[G+j B=\frac{1}{R+j X} \cdot \frac{R-j X}{R-j X}=\frac{R-j X}{R^{2}+X^{2}}\] Equating the real and imaginary parts gives
\[\boxed{G=\frac{R}{R^{2}+X^{2}}} \quad \boxed{B=-\frac{X}{R^{2}+X^{2}}}\] \[\text{Note:}~G \neq 1/R\]