RC Circuit Behavior: Understand Natural Response
Demonstrative Video
RC Circuit without Source
Transients
We will study circuits that contain sources, switches, resistances, inductances, and capacitances.
The time-varying currents and voltages resulting from the sudden application of sources, usually due to switching, are called transients.
In transient analysis, we start by writing circuit equations using developed concepts, such as KCL, KVL, node-voltage analysis, and mesh-current analysis.
The \(I-V\) relationships for inductances and capacitances involve integrals and derivatives, we obtain integro-differential equations.
These equations can be converted to pure differential equations by differentiating with respect to time.
Thus, the study of transients requires us to solve differential equations.
First Order Circuits
A first-order circuit can only contain one energy storage element (a capacitor or an inductor).
The circuit will also contain resistance.
So there are two types of first-order circuits:
RC circuit
RL circuit
The first-order circuits are characterized by first-order differential equation.
Excitation of the Circuit
There are two ways to excite the circuits.
Source-free or Natural Response:
Initial conditions of the storage elements i.e. energy initially stored in the capacitive or inductive element.
The energy causes current to flow in the circuit and is gradually dissipated in the resistors.
Although source-free circuits are by definition free of independent sources, they may have dependent sources.
Forced Response:
Excitation by independent sources.
Sources: DC, sinusoidal, exponential
The two types of first-order circuits and the two ways of exciting them add up to the four possible situations.
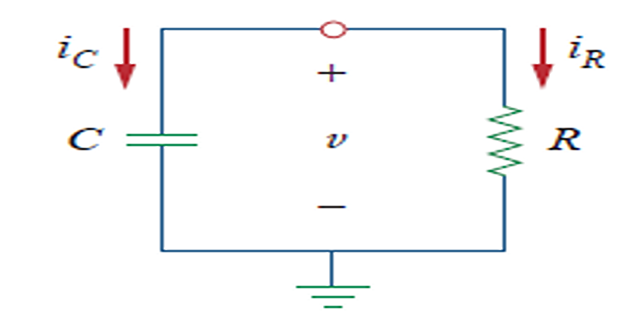
The Source-Free RC Circuit
A source-free RC circuit occurs when its dc source is suddenly disconnected.
Energy stored in capacitor is released to resistors.
\(C\) and \(R\) may come as \(C_{eq}\) and \(R_{eq}\) from a complex circuit.
Natural response of RC circuit
\[\begin{aligned} &\text{Initial condition}~v(0)=V_{0} \\ &\text{Initial energy}~w(0)=\frac{1}{2} C V_{0}^{2} \\ &\text{KCL}~~i_{C}+i_{R}=0 \\ &\Rightarrow~C \frac{d v}{d t}+\frac{v}{R}=0 \\ &\Rightarrow~\frac{d v}{d t}+\frac{v}{R C}=0 \\ &\Rightarrow~\frac{d v}{v}=-\frac{1}{R C} d t \\ &\Rightarrow~\ln (v)=-\frac{t}{R C}+\ln (A) \\ &\Rightarrow~\ln \left(\frac{v}{A}\right)=-\frac{t}{R C} \\ &\Rightarrow~v(t)=A \cdot e^{-t / R C} \end{aligned}\] \[\begin{aligned} &\text{Boundary condition}~v(0)=A=V_{0} \\ &\boxed{v(t)=V_0\cdot e^{-t / R C}} \end{aligned}\]
voltage response of the RC circuit is an exponential decay of the initial voltage.
At \(t=0~\Rightarrow~v(t)=V_0\)
As \(t~\uparrow\) \(v~\downarrow\) to zero.
The rapidity with which the voltage decreases is expressed in terms of the time constant (\(\tau\))
Time constant: Time required for the response to decay to a factor of 1/e or 36.8% of its initial value.
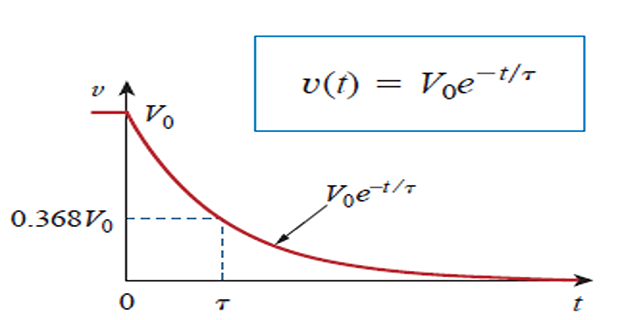
At \(t=\tau\) \[V_{0} e^{-\tau / R C}=V_{0} e^{-1}=0.368 V_{0}\]
Therefore, \(\boxed{\tau = RC}\)
Hence, \[\boxed{v(t)=V_{0} e^{-t / \tau}}\]
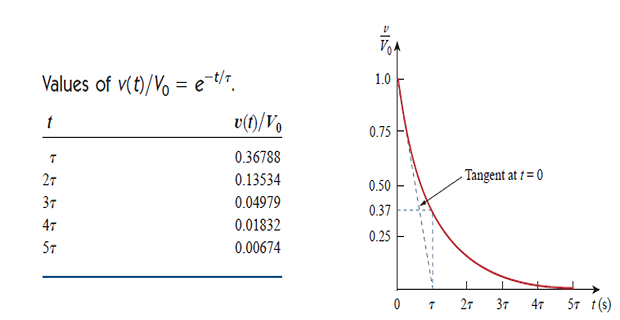
Note: \(v(t)\) is less than 1% of \(V_0\) after \(5\tau\)
Thus, it is customary to assume that the capacitor is fully discharged (or charged) after \(5\tau\).
In other words, it takes \(5\tau\) for the circuit to reach its final or steady state.
For every \(\tau\) time interval, \(v\) is reduced by 36.8% of its previous value.
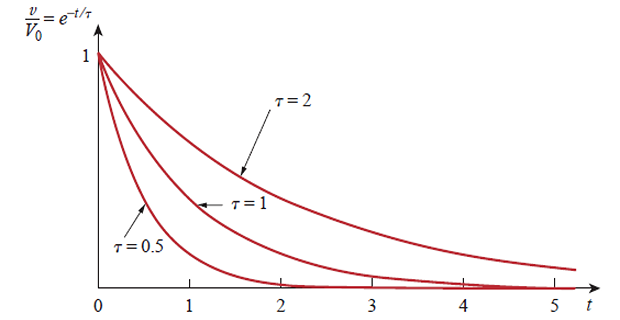
Smaller the \(\tau\), the more rapidly the voltage decreases, i.e., the faster the response to reach steady-state.
It reaches the steady state (or final state) quickly due to quick dissipation of energy stored.
\[\begin{aligned} i_{R}(t) &=\frac{v(t)}{R}=\frac{V_{0}}{R} e^{-t / \tau} \\ p(t) &=v i_{R}=\frac{V_{0}^{2}}{R} e^{-2 t / \tau} \\ w_{R}(t) &=\int_{0}^{t} p d t=\int_{0}^{t} \frac{V_{0}^{2}}{R} e^{-2 t / \tau} d t \\ &=-\left.\frac{\tau V_{0}^{2}}{2 R} e^{-2 t / \tau}\right|_{0} ^{t}=\frac{1}{2} C V_{0}^{2}\left(1-e^{-2 t / \tau}\right), \quad \tau=R C \end{aligned}\]
Notice that as \(t \rightarrow \infty, w_{R}(\infty) \rightarrow \frac{1}{2} C V_{0}^{2}\), which is the same as \(w_{C}(0)\) the energy initially stored in the capacitor.
The energy that was initially stored in the capacitor is eventually dissipated in the resistor.
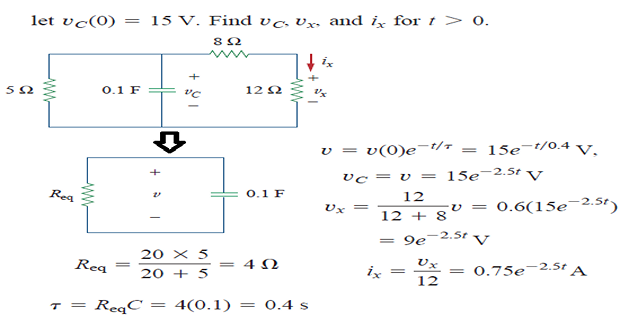
Problem Solving Steps
Determine capacitor initial voltage \(v(0)=V_0\)
Determine the time constant, \(\tau\)
Determine \(v_c(t)=v(t)=v(0)e^{-t/\tau}\)
Once \(v_c(t)\) is determined, then other variables \(i_c\), \(v_R\), and \(i_R\) can be easily solved
In finding, \(\tau=RC\), \(R=R_{TH}~\Rightarrow\) Thevenin equivalent resistance at the terminals of the capacitor; i.e. we take out \(C\) and find \(R=R_{TH}\) at its terminals.
Solved Problem